Virtual Reality: Difference between revisions
RealEditor (talk | contribs) add previously removed better language |
RealEditor (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Virtual Reality is an interactive and immersive medium that can be used to create unique experiences that are unattainable elsewhere. VR has the power to transform [[games]], [[films]] and other forms of media. Some enthusiasts call VR the "ultimate input/output device" or the "last medium" because any subsequent medium can be created within VR, using only software <ref name=”0”></ref> <ref name=”6”></ref>. | Virtual Reality is an interactive and immersive medium that can be used to create unique experiences that are unattainable elsewhere. VR has the power to transform [[games]], [[films]] and other forms of media. Some enthusiasts call VR the "ultimate input/output device" or the "last medium" because any subsequent medium can be created within VR, using only software <ref name=”0”></ref> <ref name=”6”></ref>. | ||
While [[Augmented Reality]] enhances the real world with digital content, Virtual Reality completely replaces the real world with a virtual one, creating a brand new digital environment | While [[Augmented Reality]] enhances the real world with digital content, Virtual Reality completely replaces the real world with a virtual one, creating a brand new digital environment.<ref name=”0”></ref><ref name=”6”></ref> | ||
==Main characteristics== | ==Main characteristics== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Hardware Technologies== | ==Hardware Technologies== | ||
===Head-mounted Display=== | ===Head-mounted Display=== | ||
VR is | VR is created by [[head-mounted display]]s (HMDs) such as the [[Oculus Rift]]. HMDs utilize [[stereoscopic displays]] and specialized [[lenses]] along with [[#Motion Tracking|motion tracking hardware]] to give the illusion that the user is physically inside the virtual world. | ||
To create the illusion of depth, a display is placed very close to the users' eyes, covering their entire field of view. Two images that are very similar but have different perspectives are channeled into each eye to create [[parallax]], the visual phenomenon where our brains perceive depth based on the difference in the apparent position of objects. | To create the illusion of depth, a display is placed very close to the users' eyes, covering their entire field of view. Two images that are very similar but have different perspectives are channeled into each eye to create [[parallax]], the visual phenomenon where our brains perceive depth based on the difference in the apparent position of objects. | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==Platforms== | ==Platforms== | ||
'''[[visionOS]]''' - '''[[Apple Vision Pro]]''' | '''[[visionOS]]''' - '''[[Apple Vision Pro]]''' | ||
| Line 90: | Line 88: | ||
===WebVR=== | ===WebVR=== | ||
==Virtual Reality History timeline== | ==Virtual Reality History timeline== | ||
| Line 176: | Line 170: | ||
===Virtual reality in the 21st century=== | ===Virtual reality in the 21st century=== | ||
After 1997, the public interest in VR saw a decrease in what is known as the [[first VR winter]]. Nevertheless, the first fifteen years of the 21st century had several advancements in the field of virtual reality. Computer technology, including small and powerful mobile technologies, increased in power while prices were getting more accessible <ref name=”1”></ref> <ref name=”4”></ref>. | |||
After 1997, the public interest in VR saw a decrease. Nevertheless, the first fifteen years of the 21st century had several advancements in the field of virtual reality. Computer technology, including small and powerful mobile technologies, increased in power while prices were getting more accessible <ref name=”1”></ref> <ref name=”4”></ref>. | |||
The interest in VR regained momentum after Palmer Luckey created the first prototype of the Oculus Rift, in 2011, and launched a kickstarter campaign for its development in 2012. The campaign was successful, raising $2.5 million. In March 2014, Facebook bought the company Oculus VR for $2 billion dollars. After this, virtual reality blew up, with multiple companies investing in the development of their own VR systems. The rise of smartphones with high-density displays and 3D capabilities has also enabled the development of lightweight and practical VR devices <ref name=”1”></ref> <ref name=”5”></ref> <ref name=”7”></ref>. | The interest in VR regained momentum after Palmer Luckey created the first prototype of the Oculus Rift, in 2011, and launched a kickstarter campaign for its development in 2012. The campaign was successful, raising $2.5 million. In March 2014, Facebook bought the company Oculus VR for $2 billion dollars. After this, virtual reality blew up, with multiple companies investing in the development of their own VR systems. The rise of smartphones with high-density displays and 3D capabilities has also enabled the development of lightweight and practical VR devices <ref name=”1”></ref> <ref name=”5”></ref> <ref name=”7”></ref>. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Terms]] | [[Category:Terms]] | ||
[[Category:Virtual reality]] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 14 July 2025
Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-simulated artificial multisensory 3D environment that can mimic the properties and imagery of the physical world, be completely based in fantasy, or a mix of both. It involves technology that uses computer-generated environments to simulate a physical presence in a virtual world. The system uses position-tracking and responds to the user’s inputs. In VR, the senses are temporarily fooled into believing that the artificial environment is real. The goal of a true VR experience is to create presence - the feeling of physically being somewhere else, of being in another reality [1].
Virtual Reality is an interactive and immersive medium that can be used to create unique experiences that are unattainable elsewhere. VR has the power to transform games, films and other forms of media. Some enthusiasts call VR the "ultimate input/output device" or the "last medium" because any subsequent medium can be created within VR, using only software [1] [2].
While Augmented Reality enhances the real world with digital content, Virtual Reality completely replaces the real world with a virtual one, creating a brand new digital environment.[1][2]
Main characteristics
Interactive - The user’s input controls the system and guides the behavior of the VR experience, while also modifying the virtual environment. This type of interaction engages the user, connecting him to the application in a more natural way since the environment responds directly to the stimuli [1].
Immersive - An immersive experience has to provide a sense of presence as well as a sense of engagement. Immersion can be divided into three different aspects:
1. According to Bierbaum (2000), “For a VR application to be immersive, it must be perceptually immersive by providing ‘the presentation of sensory cues that convey perceptually to users that they’re surrounded by the computer-generated environment.’” Therefore, the VR must provide the user with an all-encompassing sensory input [1].
2. The second aspect of immersion is the sense of presence. This implies that the VR experience must give the user the sense they are “in” the virtual world [1].
3. The final aspect is engagement. It is the degree “to which the user has a sense they are deeply involved in the environment.” [1]
Multisensory - providing a virtual experience that uses multiple human sensory systems increases the level of immersion. While current VR systems cannot provide a full range of stimuli to all human senses, it is expected that in the future this problem will be solved and the VR experience will be completely or almost indistinguishable from reality. The more senses are involved in the VR experience, the higher the degree of engagement and, consequently, this results in a greater sense of presence [1].
Synthetic - The environment is artificial, created by a computer in real-time [1].
Hardware Technologies
Head-mounted Display
VR is created by head-mounted displays (HMDs) such as the Oculus Rift. HMDs utilize stereoscopic displays and specialized lenses along with motion tracking hardware to give the illusion that the user is physically inside the virtual world.
To create the illusion of depth, a display is placed very close to the users' eyes, covering their entire field of view. Two images that are very similar but have different perspectives are channeled into each eye to create parallax, the visual phenomenon where our brains perceive depth based on the difference in the apparent position of objects.
Specialized lenses are placed between the display and our eyes. The lenses allow our eyes to focus on the images on the display, even though the display is only a few inches in front of our faces. Without lenses, our entire VR world would become blurry because human eyes have trouble focusing on things that are very close.[3]
The headset tracks the movement of your head and changes the images shown on the display based on it. This process creates the sensation that users are located within the virtual environment. Users of these devices are not only able to experience the computer-simulated environments but also interact with them. Various input methods, from the traditional game controllers and keyboards to the futuristic hand gestures and voice commands, are available or under development.
Motion Tracking
HMD tracks the movement of your head and updates the rendered scene based on its orientation and location. This process is similar to how we look around in real life. There are 2 types of tracking: rotational tracking and positional.
Rotational tracking tracks the 3 rotational movements: pitch, yaw, and roll. It is performed by IMUs such as accelerometers, gyroscopes and magnetometers.
Positional tracking tracks the 3 translational movements: forward/back, up/down and left/right. Positional tracking is usually more difficult than rotational tracking and is accomplished through different Types and Systems.
Motion tracking is not only used to track your head in HMDs but also used to track your hands and rest of your body through various input devices.
Input Devices
Input Devices allow the users to influence and manipulate the virtual realm they are in. These devices include traditional input methods such as gamepad, mouse and keyboard and novel devices that track the position and orientation of your hands, fingers, feet and other body parts.
Platforms
Additional Information
VR Headsets
- See also: VR Headsets
Popular VR Headsets:
- Steam Frame
- Apple Vision Pro
- Meta Quest 3S
- Meta Quest 3
- Meta Quest Pro
- Meta Quest 2
- PlayStation VR2
- Valve Index
- Oculus Rift S
- Bigscreen Beyond 2
- Bigscreen Beyond
- Varjo XR-4
- Pico 4
- Lynx R1
| Devices | Requires | Display | Resolution | Refresh Rate | Field of View | Tracking | Rotational Tracking | Positional Tracking | Update Rate | Latency | Input | Connectivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANTVR | Smartphone PlayStation 4 PC Xbox One | Aspherical lens | 1920 x 1080 | 100° diagonal | Degrees of freedom | Gyroscope Magnetometer Accelerometer | Transformable Controller | U2B (USB-2.4GHz and Bluetooth) module | ||||
| Acer Windows Mixed Reality Headset | PC | Dual LCD display | 2880 x 1440 (1440 x 1440 per eye) | 90Hz '"`UNIQ--ref-00000000-QINU`"' | 95 Degree Horizontal | 6DOF | Gyroscope Magnetometer Accelerometer | Inside-out tracking | Motion to Photon: Less than 10ms | Keyboard/Mouse Xbox One GamePad Motion Controllers | HDMI USB | |
| Apple Vision Pro | Dual Micro-OLED | 3660 × 3200 pixels per eye (23 million total pixels) | 90Hz 96Hz 100Hz | Approximately 100-120 degrees | Eye tracking Hand tracking Face tracking Room mapping | Yes | 6DoF | 12ms photon-to-photon latency | 12ms | Voice Hand gestures Eye tracking | Wi-Fi 6 Bluetooth 5.3 | |
| Apple Vision Pro M5 | 2× Micro-OLED | 3660×3200+ per eye (10% more pixels than original) | 90 Hz 120 Hz 96 Hz 100 Hz | ~100° | Inside-out 6DoF | Wi-Fi 6 Bluetooth 5.3 | ||||||
| Bigscreen Beyond 2 | Base Stations VR-ready PC VR Controllers | Dual 1-inch Micro-OLED | 2560 × 2560 per eye (5120 × 2560 total) | 75 Hz (native) 90 Hz (upscaled via DSC from 1920 × 1920) | 116° diagonal | SteamVR Tracking 6DoF) (Outside-in via SteamVR 1.0 or 2.0 base stations | Yes | Yes | Low-latency eye-tracking (on Beyond 2e) | Valve Index Controllers Requires separate VR controllers | 5 m fiber-optic tether to Link Box | |
| Bigscreen Beyond 2e | 2× Micro-OLED (RGB stripe) | 2560×2560 per eye (13.1 million pixels total) | 90 Hz | 116° | Outside-in 6DoF (SteamVR Base Stations) | USB DisplayPort | ||||||
| Daydream View | Daydream Ready Phones | 5 / 5.5 inch AMOLED (Pixel / Pixel XL) | 1920 x 1080 / 2560 x 1440 (Pixel / Pixel XL) | 60 Hz | 90° (nominal) | Degrees of freedom | Accelerator Gyrometer Proximity | None | Rotational: 1000 Hz High accuracy | Daydream Controller | ||
| FOVE | PC | 5.8 inch low persistence OLED | 2560 x 1440 | 60 - 90 Hz | 100° | Eye tracking | IMU | Their own system | Eye Tracking: 120 FPS | USB 3.0 Display port 3.5mm headphone port | ||
| Figment VR | Depends on the smartphone | Depends on the smartphone | Degrees of freedom | IMUs in Smartphone | None | |||||||
| Gear VR | Samsung phone display (Super AMOLED) | 96° (101° for later models) | 3DoF (rotational only) | Touchpad Input Devices Back button | ||||||||
| HP Reverb | LCD (dual) | 2160x2160 per eye | 90 Hz | 114° | 6DoF (inside-out 2 cameras) | Bluetooth USB 3.0 DisplayPort | ||||||
| HP Reverb G1 | VR-Ready PC | 2 x LCD | 2160 x 2160 per eye (4320 x 2160 total) | 90 Hz | Approx. 114° diagonal (Visible FoV: 95° H / 90° V ) | Inside-out tracking 6DoF | Yes | Yes | Windows Mixed Reality Motion Controllers | Bluetooth (built into headset for controllers) | ||
| HTC Vive | PC | Dual Panel | 2160 x 1200 (1080 x 1200 per eye) | 90 Hz | 110° (diagonal) | 6DOF | Gyroscope Accelerometer Laser Position Sensor | Base Stations | Rotational: 1000Hz Positional: 60Hz | Motion to Photon 7ms (no load) 15ms (medium load) | Controllers in both hands | 2 HDMI ports 2 USB ports 1 headphone jack |
| HTC Vive Developer Editions | PC | Dual Panel | 2160 x 1200 1080 x 1200 per eye | 90 Hz | 110° (diagonal) | 6DOF | Gyroscope Accelerometer Laser Position Sensor | Base Stations | ?? | ?? | Controllers in both hands | 2 HDMI ports 2 USB ports 1 headphone jack |
| HTC Vive Pro | PC | Dual Panel | 2880 x 1600 (1440 x 1600 per eye) | 90 Hz '"`UNIQ--ref-00000006-QINU`"' | 110° (diagonal) | 6DOF | Gyroscope Accelerometer Laser Position Sensor | Base Stations | Rotational: TBC Positional: TBC | Motion to Photon TBC | Controllers in both hands | DisplayPort 1.2 USB-C 3.0 port Bluetooth (Version TBD) (TBD: 1 headphone jack???) |
| Impression Pi | Smartphone | Depends on smartphone | Depends on the smartphone | 6 DOF | IMU Board | IMU Board Infared Cameras? IR Projector? | ||||||
| IonVR | 2 AAA batteries Smartphone (4.5"-6" screen) | Smartphone display (Super AMOLED or IPS) | Min. 720p resolution 1080p recommended 2K ideal | 80-100 degrees | Rotational (3DOF) Positional (6DOF with Intel RealSense) | Yes (3-axis IMU) | Yes (with Intel RealSense ZR300) | Compatible with Bluetooth controllers | ||||
| LG 360 VR | LG G5 | 1.88" IPS LCD x 2 EA 920 x 720 per Eye 639 ppi Real RGB | 960x720 pixels at 693ppi (per eye) | 60Hz | Motion to Photon: over 50ms | |||||||
| Lenovo Windows Holographic HMD | PC | 1440x1440-pixel OLED display | Inside-out Tracking | Two Cameras | Input Devices | HDMI and USB Connectors | ||||||
| Lynx R1 | None (Standalone device) | Dual LCD (binocular) | 1600×1600 per eye | 90 Hz | 90°×90° (circular) | 6DOF inside-out tracking | Yes (6DOF) | Yes (6DOF) | Hand tracking Optional 6DOF controllers based on Finch Technologies Shift | Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) Wi-Fi 5 DisplayPort Alt-Mode) USB-C (3.1 Gen1 | ||
| Lynx-R1 | 2× LCD | 1600×1600 per eye | 90 Hz | 90° (circular) | Inside-out 6DoF (6 cameras) | Bluetooth Wi-Fi USB-C | ||||||
| Meta Quest 3 | Meta account | 2 x LCD ("4K+ Infinite Display") | 2064×2208 per-eye | 90Hz 72Hz 120Hz (144Hz experimental) | 110° (horizontal) 96° (vertical) | Inside-out tracking 6DoF | Yes (IMU-based) | Yes (SLAM-based) | 2 × Meta Quest Touch Plus Controllers | Bluetooth 5.2 LE Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax with 6GHz) | ||
| Meta Quest 3S | Meta account | Single LCD | 1832 x 1920 pixels per eye | Up to 120Hz | Inside-out tracking 6DoF | Yes | Yes | Hand tracking Touch Plus controllers | Bluetooth Wi-Fi 6E | |||
| NVIS nVisor SX60 | PC/Workstation with dual-link DVI or VGA | LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon) | 1280x1024 per eye (SXGA) | 60 Hz | 60° diagonal | 3 DoF (6 DoF with optional external trackers) | Yes | Optional (with external trackers) | Up to 180 Hz (tracker-dependent) | VGA DVI RS-232 | ||
| OSVR HDK1 | PC | 5.5 inch LCD (1.0) 5.5 inch low-persistence OLED (1.1 - 1.3) | 1920 x 1080 960 x 1080 per eye | 60 Hz (1.0 - 1.2) 120 Hz (1.3) | 100° (nominal) 90° (H and V) | 6DOF Degrees of freedom | Gyroscope Magnetometer Accelerometer | IR-LED faceplate and External Infrared Camera | Rotational: 400Hz Positional: 100 Hz | ?? | Gamepads Mouse and Keyboard Leap Motion VR | 1 external and 2 internal USB 3.0 ports |
| OSVR HDK2 | PC | 5.5 inch OLED | 2160 x 1200 (1080 x 1200 per eye) | 90 Hz '"`UNIQ--ref-00000003-QINU`"' | 110 degrees | 6DOF Degrees of freedom | Gyroscope Magnetometer Accelerometer | ??? | Rotational: 400Hz Positional: 100 Hz | ?? | ??? | 1 external and 2 internal USB 3.0 ports |
| Oculus Quest 2 | LCD (single panel) | 1832x1920 per eye | 72/80/90/120 Hz | 97° | 4 cameras) 6DoF (inside-out | |||||||
| Oculus Rift | PC | Dual OLED Panels | 2160 x 1200 (1080 x 1200 per eye) | 90 Hz | 110° (diagonal) | 6DOF | Gyroscope Magnetometer Accelerometer | Oculus Sensor | Rotational: 1000Hz Positional: 60Hz | Motion to Photon: less than 5ms | Oculus Touch Xbox One controller Oculus Remote | HDMI USB |
| Oculus Rift S | VR-Ready PC | Fast-switch LCD | 2560×1440 (1280×1440 per eye) | 80Hz | 115° | Inside-out tracking (6DOF) | Yes | Oculus Insight | Oculus Touch | USB 3.0 DisplayPort 1.2 | ||
| Oculus Santa Cruz | Inside-out tracking | Input Devices | 1 HDMI 2 USB 3.0 Ports | |||||||||
| Philips Scuba | Sony PlayStation Nintendo 64 Sega Saturn DVD player PC with composite video output | Approx. 0.7 inches each Dual AMLCD (Active Matrix LCD) | 263 × 230 pixels per eye | 60 Hz (NTSC) 50 Hz (PAL) | 50° diagonal (40° horizontal × 30° vertical) | 3 DoF Non-positional | Yes (Gyroscope Based) | No | Control box with power button Brightness/contrast controls Volume control | Stereo audio input RCA composite video input | ||
| Pico 4 Pro | 2× LCD | 2160×2160 per eye | 90 Hz 72 Hz | 105° | Inside-out 6DoF (4 cameras) | USB-C Bluetooth 5.1 Wi-Fi 6 | ||||||
| Pico 4 Ultra Enterprise | 2× 2.56" LCD | 2160×2160 per eye (4K+) | 90 Hz | 105° | Inside-out 6DoF (4 cameras) | Bluetooth USB-C Wi-Fi 7 | ||||||
| Pico G2 | 3K LCD Blue ray reduction | 2880 x 1600 | 90Hz 615 ppi | 101 degrees | Degrees of freedom | 1 3DOF Controller | N/A | |||||
| Pico G3 | LCD | 3664×1920 (combined) | 72 Hz 90 Hz (dynamic) | ~101° | 3DoF (head rotation only) | Bluetooth Wi-Fi USB-C | ||||||
| Pico Neo 3 Pro | 4k 5.5" 3664 x 1920 LCD PPI 773 | 72/90Hz | Fresnel 98 degrees | 6DOF Inside-out tracking | 2 Updated Pico Neo Controllers | Displayport | ||||||
| Pico Neo CV | Dual 1.5K AMOLED | 1500 x 1500 pixels/eye | 90Hz | 102 degrees | 6 Degrees of Freedom (6DoF) | |||||||
| Pimax 5K Super | 2x LCD (RGB stripe matrix) | 2560x1440 per eye (5120x1440 combined) | 90 Hz 120 Hz 160 Hz 144 Hz 180 Hz (experimental) | 200° diagonal 170° horizontal 115° vertical (varies by mode) | 6DoF (SteamVR Lighthouse 1.0/2.0) | USB DisplayPort 1.4 Power | ||||||
| Pimax 8K | Custom low-latency LCD screen | 8K (4K for each eye) | Monocular 75Hz / (Up to 90Hz although struggling to better 80Hz) (Both eyes 150Hz / 180Hz through Brainwarp) | 200-degree FOV | Gesture Tracking (optional) | Yes | 18ms (Low MTP Latency) | |||||
| Pimax 8KX | 2× 4K CLPL LCD | 3840×2160 per eye (native 4K) | 75 Hz 90 Hz (native) 114 Hz (upscale) | 200° diagonal (170° horizontal 115° vertical) | Lighthouse (SteamVR base stations) | USB 3.0 DisplayPort 1.4 | ||||||
| Project Alloy | ||||||||||||
| Samsung Gear VR (2015/2016) | All Samsung Smartphones 2015 and newer | 5.7 / 5.1 inch Super AMOLED (RGBG PenTile) | 2560 x 1440 1280 x 1440 per eye | 60 Hz | 96° (nominal) | Degrees of freedom | Accelerator Gyrometer Proximity | None | Rotational: 1000 Hz High accuracy | Motion to Photon: Less than 6 ms | Back Button Volume Key Touchpad Focus adjustment wheel | MicroUSB to the smartphone |
| Samsung Gear VR Innovator Edition | Galaxy Note 4 Galaxy S6 Galaxy S6 Edge | 5.7 / 5.1 inch Super AMOLED (RGBG PenTile) | 2560 x 1440 1280 x 1440 per eye | 60 Hz Low-persistence | 96° (nominal) | Degrees of freedom | Gyroscope Magnetometer Accelerator | None | Rotational: 1000 Hz High accuracy | Motion to Photon: Less than 20 ms | Touch Pad Back Button Volume Key | MicroUSB to the smartphone |
| Shiftall MeganeX Superlight 8K | 2× 1.35" Micro-OLED (4K per eye) | 3552×3840 per eye (8K total) | 90 Hz | ~90° | Outside-in 6DoF (SteamVR Lighthouse) | USB-C DisplayPort | ||||||
| Simula One | None (standalone) PC for tethered mode Bluetooth keyboard & mouse (optional) | Dual 2448×2448 RGB-stripe LCD high-fidelity panels | 2448×2448 per eye (4896×2448 total) | 90 Hz (up to 120 Hz capable panels mentioned previously) | ≈100° diagonal | Inside-out tracking (6DOF) | Yes (3DOF via IMU) | Yes (6DOF) | Keyboard and mouse compatible (via Bluetooth or USB) | Wi-Fi 6E Bluetooth 5.2 | ||
| StarVR | PC | Dual 5.5" LCD Quad HD Displays | 5120 x 1440 (2560 x 1440 per eye) | 210° (horizontal) 130° (vertical) | 6DOF | Gyroscope Magnetometer Accelerometer | External optical sensor with fiducial markers | |||||
| Steam Frame | PC for streaming (optional) Included wireless adapter | Dual 2160×2160 LCD panels | 2160×2160 per eye | 72–120 Hz (144 Hz experimental) | Stated 110° horizontal × 110° vertical | Inside‑out 6DoF SLAM (4 external monochrome cameras + IR illuminators) | 6DoF IMU + optical | Inside‑out optical tracking | 10–20 ms typical end‑to‑end streaming (claimed) | Steam Frame Controllers; optional Bluetooth gamepads Keyboard and mouse | Bluetooth 5.3 Wi‑Fi 7 (headset) Bundled Wi‑Fi 6E PC adapter | |
| Sulon Q | PC | OLED | 2560x1440 pixels | Gamepads Mouse and Keyboard Dual noise-suppressing embedded microphones Controllers compatible with Windows 10 | Bluetooth 4.0 Wi-Fi 802.11ac | |||||||
| Takara HMD Dynovisor | NTSC composite/AV console External power supply | Sony Active TFT LCD | 180 000 pixels (320x240 per eye Estimated) | 30 Hz | 120° diagonal | 3 DoF (gyroscope-based) | Yes (pitch Yaw Roll) | No | Atari Jaguar controllers | Composite video (NTSC) Audio (Red/White RCA) Proprietary Atari Jaguar connection | ||
| VPL EyePhone | High-end computer system (Silicon Graphics workstation) Polhemus magnetic tracker | Dual active-matrix LCD panels | 185 × 138 (Model 1) 320 × 240 (Model 2 LX) 720 × 480 (Model HRX) per eye | 30 Hz | 90° (Model 1) 108° (Model 2 LX) 106° (Model HRX) | 3 DoF electromagnetic (Polhemus FASTRAK) | Yes | No | 60 Hz | Less than 50 ms (with SGI rendering) | DataGlove (sold separately) | Wired to computer (NTSC composite signals) |
| Valve Index | Windows 10 SteamOS Or Linux; NVIDIA GeForce GTX 970 / AMD RX 480 or better | Dual 1440×1600 RGB LCD panels | 2880×1600 (combined) | 80/90/120/144Hz | ~130 degrees (diagonal) | SteamVR Tracking (Lighthouse 2.0) | 6 DOF | 6 DOF | Valve Index Controllers (included) | USB 3.0 DisplayPort 1.2 | ||
| Varjo Aero | High-end PC | Mini-LED | 3840×3744 per eye | 90 Hz (120 Hz experimental) | 120° × 105° (H×V) | Inside-out (4 cameras) | 6DOF | 6DOF | 200 Hz | Less than 15ms (VR) ~22ms (passthrough) | Hand tracking SteamVR controllers | USB-C (Thunderbolt 4 compatible) |
| Varjo VR-2 | High-end PC | Dual OLED displays per eye (Bionic Display) | Focus: 1920×1080 per eye Context: 1440×1600 per eye | 90 Hz (both displays) | 87° | SteamVR 1.0/2.0 | 6DOF | 6DOF | 1000 Hz | Less than 20ms | Compatible with SteamVR controllers | DisplayPort 1.4 USB 3.0+ |
| Varjo XR-3 | High-end PC | UOLED (focus) + LCD (peripheral) | Focus: 1920×1920 per eye Context: 2880×2720 per eye | 90 Hz | 115° | SteamVR 2.0 Inside-out (beta) | 6DOF | 6DOF | 1000 Hz | Less than 20ms (VR) Less than 20ms (passthrough) | Compatible with SteamVR controllers | DisplayPort 1.4 USB-C 3.0 |
| Varjo XR-4 | High-end PC | Mini-LED | 3840×3744 per eye | 90 Hz (120 Hz experimental) | 120° × 105° (H×V) | Inside-out (4 cameras) | 6DOF | 6DOF | 200 Hz | Less than 15ms (VR) ~22ms (passthrough) | Hand tracking SteamVR controllers | USB-C (Thunderbolt 4 compatible) |
| Varjo XR-4 Focal Edition | 2× Mini-LED LCD | 3840×3744 per eye (4K×4K) | 90 Hz | 120° × 105° | Inside-out + SteamVR (hybrid) | USB-C DisplayPort | ||||||
| Virtual Boy | Six AA batteries or AC adapter | Dual 1×224 LED array with oscillating mirrors | 384×224 per eye | 50.27 Hz | ~50° horizontal | None | No | No | Virtual Boy Controller | Controller port Cartridge slot EXT port (unused) | ||
| Virtual i-O i-glasses! | ||||||||||||
| Vive Cosmos | LCD (RGB Dual) | 1440x1700 per eye | 90 Hz | 110° | 6DoF (inside-out 6 cameras) | |||||||
| Vive Flow | LCD (dual) | 1600x1600 per eye | 75 Hz | 100° | 6DoF (inside-out) | Wi-Fi Bluetooth 5.0 | ||||||
| Vive Focus | AMOLED (single panel) | 2800x1600 | 75 Hz | 110° | 6DoF (inside-out 2 cameras) | Bluetooth Wi-Fi USB-C (OTG) | ||||||
| Vive Focus 3 | LCD | 2448x2448 per eye (5K) | 90 Hz | 120° | 4 cameras) 6DoF (inside-out | |||||||
| Vive Focus Plus | AMOLED (dual) | 1440x1600 per eye | 75 Hz | 110° | 6DoF (inside-out + ultrasonic controllers) | Wi-Fi 5GHz USB 3.1 Type-C | ||||||
| Vive Focus Vision | Dual) LCD (fast-switch | 2448x2448 per eye | 90 Hz (120 Hz planned via DisplayPort) | 120° | 4 cameras) 6DoF (inside-out | DisplayPort Bluetooth 5.2 Wi-Fi 6/6E USB-C (2x) | ||||||
| Vive Pro 2 | LCD (dual) | 2448x2448 per eye | 120 Hz | 116° (marketed 120°) | SteamVR 2.0 (outside-in) | USB 3.0 DisplayPort | ||||||
| Vive Pro Eye | OLED (dual) | 1440x1600 per eye | 90 Hz | 110° | SteamVR 2.0 (outside-in) | USB 3.0 DisplayPort | ||||||
| Wearality Sky | Smartphone | Depends on smartphone | Depends on smartphone | 150° | Degrees of freedom | IMUs in Smartphone | None |
- To make changes to the table, please edit the the infobox of the corresponding device. See Template:Device Infobox for reference.
Apps
Developer Resources
Game Engines
WebVR
Virtual Reality History timeline




Virtual reality has a long history of development. While the main advancements happened after the introduction of electronics and computer technology, there are precursors to the ideas and implementation of VR that date as far back as the 1800s. For example, focusing solely on VR as a means of creating the illusion of being someplace else, then the earliest attempts at virtual reality could be considered the panoramic murals (or 360-degree murals). These would fill the viewer’s field of vision with the intention of making them feel a sense of presence at a certain historical event or scene [4] [5].
What follows is a timeline of the main historical dates and events in the development of VR.
1838 - Stereoscopic viewers and photos
Charles Wheatstone demonstrated that the brain processes different two-dimensional images for each eye into a single three dimensional object (Figure 1). The stereoscope was invented in the same year and used twin mirrors to project a single image. When viewing two side by side stereoscopic images through a stereoscope, it gave the sense of depth and immersion [4] [5] [6].
In 1839, William Gruber also patented the View-Master stereoscope which was used for “virtual tourism” and still is produced today. The design principles of the stereoscope can still be found in the Google Cardboard and low-budget VR headsets for smartphones [4] [6].
It could be argued that since the creation of stereoscopic images, people have been interested in making images more three dimensional to enrich its experience [6].
1929 - Link Trainer
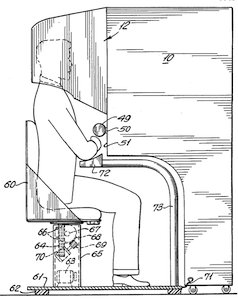
Edward Link creates the first commercial flight simulator - the Link Trainer (Figure 2). It was entirely electromechanical, “controlled by motors that linked to the rudder and steering column to modify the pitch and roll.” It had a small motor-driven device that simulated turbulence and other disturbances. These flight simulators were used by over 500,000 pilots during World War II for initial training and improving skills [4] [6].
1936 - Pygmalion’s Spectacles
Science fiction writer Stanley G. Weinbaum wrote a short story - Pygmalion’s Spectacles - that had the idea of a pair of goggles that allowed the user to experience a different world through holographic recordings, smell, taste, and touch. This concept can be easily equated to the VR devices that are currently available or under development [4] [6] [7].
1956 - The Sensorama
Cinematographer Morton Heilig develops the Sensorama, which was patented only in 1962 and might be considered the first true VR system. It was an arcade-style cabinet that stimulated all the senses. It had a stereoscopic 3D display, stereo speakers, vibrating seat, fans, and a scent producer. It was intended to fully immerse the person in a film. Heilig created six short films for his invention titled Motorcycle, Belly Dancer, Dune Buggy, Helicopter, A date with Sabina and I’m a coca cola bottle! Heilig intended the Sensorama to be one in a line of products for the “cinema of the future”. Unable to secure financial backing, his vision never became reality [4] [5] [7] [8] [2].
1960 - First VR Head-Mounted Display
After the Sensorama, Morton Heilig invented the first example of a virtual reality headset - the Telesphere Mask. It only worked with non-interactive films and didn’t have motion tracking. Nevertheless, the headset provided stereoscopic 3D and wide vision with stereo sound [4] [5].
1961 - First motion tracking HMD
The true precursor of the HMDs available today was developed by two Philco Corporation engineers, Comeau and Bryan. It was called Headsight and it incorporated a video screen for each eye and a magnetic motion tracking system. This system was linked to a closed circuit camera. The device wasn’t developed for virtual reality applications. Instead, its goal was to allow immersive remote viewing of dangerous situations by the military. The head movements of the used would be replicated by a remote camera, allowing him to look around the environment. While the Headsight was a step in the evolution of the virtual reality headset, it lacked the integration of a computer and image generation [4].
1965 - The Ultimate Display
Ivan Sutherland developed the concept of the “Ultimate Display”. This device could simulate the natural world so realistically that a user could not tell the difference between actual reality and virtual reality. The concept comprised of a virtual world viewed through an HMD and had augmented 3D sound and tactile feedback; computer hardware that created the virtual environment and maintained it in real time; and interactivity between users and objects from the VR world in a realistic way. Sutherland suggested that the device would serve as a “windows into a virtual world”, and his idea would become a core blueprint for the concepts that encompass current VR [4] [5] [2].
1968 - Sword of Damocles
Ivan Sutherland and Bob Sproull created the Sword of Damocles, an HMD that was held by a mechanical arm mounted on a ceiling. The device was connected to a computer and displayed simple wireframe graphics to the user. The arm tracked the user’s head movements but was difficult to use. The contraption was also too heavy and bulky for comfortable use [4] [7] [2].
1969 - Artificial Reality
Myron Kruegere developed a series of experiences called “Artificial Reality”. He developed computer-generated environments that responded to the people in it. He created several projects such as Glowflow, Metaplay, and Psychic Space leading to the development of the Videoplace technology. This enabled communication between people at a distance in a responsive computer-generated environment [4].
1975 - Videoplace
Myron Kruegere created the Videoplace, which was the first interactive VR platform. The virtual reality surrounded the user and responded to movements and actions without the use of goggles or gloves. The Videoplace was a mix of several other artificial reality systems that he had developed [2] [9].
1982 - Sayre gloves
The Sayre glove was the first wired glove. It was invented by Daniel J. Sandin and Thomas Defanti from an idea by Richard Sayre. Both scientists were from the Electronic Visualization Laboratory at the University of Illinois, Chicago. The glove used light emitters and photocells in the fingers. When flexed, the quantity of light reaching the photocell changed, translating the finger movements into electrical signals [7].
1985 - NASA project
The Virtual Environment Workstation Project at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Mountain View, California, was founded with the purpose of producing a VR system that allowed astronauts to control robots outside a space station (Figure 4). The HMD that was developed had super-wide optics (almost an 180-degree field of view) [7].
1987 - The “Virtual Reality” name is coined
Before this date, even though there had been developments in VR, there wasn’t a term to describe the field. In 1987, Jaron Lanier (founder of the Visual Programming Lab, VPL) finally coined the term “virtual reality”. Lanier, through his company, developed a range of VR gear like the Dataglove and the EyePhone headset. The company also made the first surgical simulator, the first vehicle prototyping simulator, and the first architecture simulators [4] [5] [7].
1991 - Virtuality Group
By this time, VR devices started to be available to the public (although owning cutting-edge VR was still out of reach). The Virtuality Group launched several arcade games and machines in which players would use a set of VR goggles (Figure 5). The machines had immersive stereoscopic 3D visuals, handheld joysticks, and some unit were networked together for multiplayer gaming. There were some discussions about bringing Virtuality to Atari’s Jaguar console, but the idea was abandoned [4] [7].
1993 - Sega’s virtual reality headset
At the Consumer Electronics Show in 1993, Sega announced a virtual reality headset for the Sega Genesis console. The prototype had head tracking, stereo sound and LCD screens in the visor. The company intended to have a general release of the product but technical difficulties stopped that from happening and the headset would remain in the prototype phase [4] [7].
1995 - Nintendo Virtual Boy
The Virtual Boy was a 3D gaming console, marketed as the first portable console that could display 3D graphics. It was released in Japan and North America, and it was a commercial failure for the Japanese company. Some of the reasons for the failure were the lack of color in graphics (only red and black), lack of software support, and difficulty in using the console in a comfortable position. Production of the console was halted in 1996 [4] [7].
Virtual reality in the 21st century
After 1997, the public interest in VR saw a decrease in what is known as the first VR winter. Nevertheless, the first fifteen years of the 21st century had several advancements in the field of virtual reality. Computer technology, including small and powerful mobile technologies, increased in power while prices were getting more accessible [4] [7]. The interest in VR regained momentum after Palmer Luckey created the first prototype of the Oculus Rift, in 2011, and launched a kickstarter campaign for its development in 2012. The campaign was successful, raising $2.5 million. In March 2014, Facebook bought the company Oculus VR for $2 billion dollars. After this, virtual reality blew up, with multiple companies investing in the development of their own VR systems. The rise of smartphones with high-density displays and 3D capabilities has also enabled the development of lightweight and practical VR devices [4] [8] [9].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Bierbaum, A.D. (2000). VR Juggler: A Virtual Platform for Virtual Reality Application Development. Masters of Science Thesis, Iowa State University, Iowa
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Mazuryk, T. and Gervautz, M. (1996). Virtual Reality - History, applications, technology and Future (Technical Report). Retrieved from https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/1996/mazuryk-1996-VRH/TR-186-2-96-06Paper.pdf
- ↑ http://doc-ok.org/?p=1360
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 Virtual Reality Society. History of Virtual Reality. Retrieved from https://www.vrs.org.uk/virtual-reality/history.html
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 The Franklin Institute. History of Virtual Reality. Retrieved from https://www.fi.edu/virtual-reality/history-of-virtual-reality
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Gemsense. Virtual Reality: History, projections and developments. Retrieved from http://gemsense.cool/virtual-reality-developments/
- ↑ 7.00 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 Evenden, I. (2016). The history of virtual reality. Retrieved from http://www.sciencefocus.com/article/history-of-virtual-reality
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Robertson, A. and Zelenko, M. Voices from a virtual past. Retrieved from https://www.theverge.com/a/virtual-reality/oral_history
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Freefly VR. Time travel through virtual reality. Retrieved from https://freeflyvr.com/time-travel-through-virtual-reality/

