Vergence-accommodation conflict: Difference between revisions
Copied from XVR Wiki: https://www.xvrwiki.org/wiki/Vergence-accommodation_conflict Tag: Reverted |
RealEditor (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Vergence accommodation conflict image.png|thumb|right|250px|Vergence-accommodation conflict in VR compared to real-world vision]] | |||
'''Vergence-accommodation conflict''' ('''VAC'''), also known as '''accommodation-vergence conflict''' or sometimes '''accommodation-vergence mismatch''', is a visual and perceptual phenomenon that occurs when the [[Brain|brain]] receives mismatching cues between the distance to which the eyes are pointed or converged ([[Vergence|vergence]]) and the distance at which the eyes' lenses are focused ([[Accommodation (eye)|accommodation]]).<ref name="Hoffman2008">Hoffman D M, Girshick A R, Akeley K, Banks M S. (2008). “Vergence–accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue.” ''Journal of Vision'', 8 (3): 33 (1‑30). doi:10.1167/8.3.33. PMID 18484839. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18484839/</ref><ref name="Kreylos2014VAC">{{cite web |last=Kreylos |first=Oliver |title=Accommodation and Vergence in Head-mounted Displays |url=http://doc-ok.org/?p=1602 |website=Doc-Ok.org |date=2014-04-13}}</ref> Because natural viewing conditions tightly couple these two mechanisms, breaking that link is a primary cause of visual discomfort and performance issues in modern [[Virtual reality|virtual reality]] (VR), [[Augmented reality|augmented reality]] (AR), and other [[Stereoscopy|stereoscopic]] 3-D displays, including nearly all mainstream [[Head-Mounted Display|head-mounted displays]] (HMDs).<ref name="Hoffman2008" /> | |||
==Physiological Basis== | |||
When fixating on an object in the real world, the human [[Visual system|visual system]] simultaneously performs two key actions: | |||
* '''[[Vergence]]''': The two eyes rotate inwards ([[Convergence (eye)|convergence]]) or outwards ([[Divergence (eye)|divergence]]) via the [[Extraocular muscles|extraocular muscles]] so their lines of sight intersect at the target object, enabling single [[Binocular vision|binocular vision]]. This response is primarily driven by [[Binocular disparity|retinal disparity]]. | |||
* '''[[Accommodation (eye)|Accommodation]]''': The [[Ciliary muscle|ciliary muscle]] adjusts the shape and thus the [[Optical power|optical power]] of the [[Crystalline lens|crystalline lens]] within each eye to bring the image of the target object into sharp focus on the [[Retina|retina]]. This response is primarily driven by retinal blur. | |||
In | In natural vision, these two systems are tightly linked through fast, reciprocal neurological signals known as the [[Accommodation reflex|accommodation-vergence reflex]].<ref name="Kreylos2014VAC" /><ref name="Kramida2016">Kramida G, Varshney A. (2016). “Resolving the vergence–accommodation conflict in head‑mounted displays.” ''IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics'', 22 (7): 1912‑1931. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2015.2473855. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2015.2473855</ref> This coupling ensures that the eyes focus at the same distance they are pointed, allowing for clear, comfortable, and efficient vision. Stereoscopic displays disrupt this natural coupling because binocular disparity cues drive the vergence system to the ''simulated'' depth of a virtual object, while the accommodation system is driven by blur cues to focus on the ''physical'' display surface, which is typically at a fixed optical distance.<ref name="Kramida2016" /> | ||
The | ==Causes / Occurrence in Display Technologies== | ||
The vergence-accommodation conflict is inherent in display technologies where the perceived depth of content differs from the physical or optical distance of the display surface: | |||
* '''Fixed-focus HMDs''': Nearly all consumer VR and many AR headsets use internal display screens (like OLED or LCD) viewed through lenses. These lenses create a [[virtual image]] of the screens, making them appear to be located at a fixed focal distance, typically between 1.3 and 2 meters (though this varies).<ref name="Kreylos2013HMD">{{cite web |last=Kreylos |first=Oliver |title=Head-mounted Displays and Lenses |url=http://doc-ok.org/?p=1360 |website=Doc-Ok.org |date=2013-07-24}}</ref> Consequently, viewers must accommodate (focus their eyes) to this fixed plane to see a sharp image, regardless of the perceived depth of virtual objects. However, stereoscopic rendering creates virtual objects that appear at various depths by presenting slightly different images to each eye, requiring the viewer's eyes to converge or diverge (vergence). Objects rendered virtually nearer than the fixed focal plane induce a ''positive VAC'' (eyes converge more than they accommodate), while objects rendered virtually farther induce a ''negative VAC'' (eyes converge less than they accommodate).<ref name="Shibata2011">Shibata T, Kim J, Hoffman D M, Banks M S. (2011). “The zone of comfort: Predicting visual discomfort with stereo displays.” ''Journal of Vision'', 11 (8): 11. doi:10.1167/11.8.11. PMC 3369815. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3369815/</ref> | |||
* '''[[3D television|3D Cinema and Television]]''': VAC also occurs here, but symptoms are often milder. The screen is typically farther away, the [[Field of view|field of view]] is smaller, and content creators can limit disparities to keep virtual objects within a "zone of comfort" relative to the screen distance.<ref name="ISO2015">International Organization for Standardization. (2015). ''ISO 9241‑392:2015 - Ergonomics of human‑system interaction – Part 392: Ergonomic requirements for the reduction of visual fatigue from stereoscopic images''. https://www.iso.org/standard/60317.html</ref> | |||
* '''[[Optical see-through display|Optical See-Through (OST) AR]]''': In OST AR glasses, virtual images (often at a fixed focus) are overlaid onto the real world. This creates a conflict not only between vergence and accommodation for virtual objects but also a potential mismatch between focusing on real-world objects at various distances and the fixed focus of the virtual overlay. This can introduce depth discontinuities, reduce the perceived registration accuracy of virtual objects, and cause discomfort.<ref name="Zhou2021">Zhou Y, Li X, Yuan C. (2021). “Vergence‑accommodation conflict in optical see‑through display: Review and prospect.” ''Results in Optics'', 5: 100160. doi:10.1016/j.rio.2021.100160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rio.2021.100160</ref> | |||
==Effects and Symptoms== | |||
The sustained conflict between vergence and accommodation forces the visual system and brain to work harder, potentially leading to a range of negative effects:<ref name="Kramida2016" /><ref name="Hoffman2008" /> | |||
* '''[[Visual fatigue]] / Eyestrain''': Tired, aching, or burning eyes resulting from the prolonged effort to resolve conflicting cues. | |||
* '''[[Headache]]s'''. | |||
* '''Blurred Vision''': Difficulty maintaining sharp focus on virtual objects, especially those perceived as very near or very far relative to the display's fixed focal plane. | |||
* '''[[Diplopia]] (Double Vision)''': Incorrect vergence responses due to the conflict can sometimes lead to seeing double images. | |||
* '''Focusing Problems''': Difficulty rapidly refocusing between virtual objects at different apparent depths because the natural reflex is disrupted. Users may also experience lingering focus issues or unusual visual sensations after removing the HMD. | |||
* '''[[Virtual Reality Sickness|VR Sickness]] / Discomfort''': VAC is considered a significant contributor to symptoms like nausea, dizziness, and general discomfort associated with VR/AR use. | |||
* '''Reduced Visual Performance''': Measurable degradation in tasks requiring fine depth judgments, reduced reading speed, slower visuomotor reaction times, and increased time required to fuse binocular images.<ref name="Hoffman2008" /><ref name="Lin2022">Lin C‑J, Chi C‑F, Lin C‑K, Chang E‑C. (2022). “Effects of virtual target size, position and parallax on vergence‑accommodation conflict as estimated by actual gaze.” ''Scientific Reports'', 12: 20100. doi:10.1038/s41598‑022‑24450‑9. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598‑022‑24450‑9</ref> | |||
* '''[[Focal Rivalry]]''': Particularly in AR, the conflict between focusing on a real-world object and a virtual object projected at a different focal distance can make it difficult or impossible to see both sharply simultaneously. | |||
The severity of these symptoms varies significantly between individuals and depends on factors such as the magnitude of the VAC (the difference between vergence and accommodation distances), the duration of exposure, the nature of the visual content, and individual visual capabilities. Conflicts below approximately 0.4 to 0.6 [[Diopter|diopters]] are often tolerated, but larger conflicts, especially for near-field virtual objects (within arm's reach), become increasingly problematic.<ref name="Shibata2011" /><ref name="ISO2015" /> | |||
==Measurement== | |||
VAC can be quantified by comparing the optical power (measured in [[Diopter|diopters]], D, which is the reciprocal of distance in meters) required for accommodation versus the optical power corresponding to the vergence distance.<ref name="Kramida2016" /> | |||
* `VAC (Diopters) = | (1 / Accommodation Distance (m)) - (1 / Vergence Distance (m)) |` | |||
For example, if an HMD has a fixed focus set to 2 meters (requiring 1/2.0 = 0.5 D of accommodation) and displays a virtual object that appears to be 0.5 meters away (requiring 1/0.5 = 2.0 D of vergence), the VAC magnitude is |0.5 D - 2.0 D| = 1.5 D. | |||
== | ==Mitigation Strategies== | ||
Addressing VAC is a major focus of VR and AR research and development. Strategies fall into two main categories: content design and technological solutions. | |||
===Content and Interaction Guidelines=== | |||
Careful design can minimize VAC-induced discomfort in fixed-focus displays: | |||
# '''Limit Depth Range''': Keep critical interactive content and prolonged visual targets within the "zone of comfort," typically corresponding to less than ~0.6 D of VAC for foreground objects (closer than the focal plane) and ~1.0 D for background objects (farther than the focal plane).<ref name="ISO2015" /><ref name="Shibata2011" /> | |||
# '''Avoid Rapid Depth Changes''': Avoid sudden disparity jumps (> 1 D) or rapid oscillations in depth for prominent objects. Allow the visual system time (at least 500 ms) to adjust to significant depth changes.<ref name="Kramida2016" /> | |||
# '''Optimize UI Placement''': Present user interface elements, text, and critical information at or slightly behind the display's native focal plane where VAC is zero or negative (which is generally better tolerated).<ref name="Shibata2011" /> | |||
# '''Simulate Blur''': When hardware cannot provide correct focus cues, incorporate [[Gaze-contingent display|gaze-contingent]] [[Depth of field|depth-of-field]] rendering (simulating blur for objects not being looked at) to provide [[Monocular cues|monocular]] depth information that aligns better with vergence, potentially reducing cue conflicts.<ref name="Koulieris2017">Koulieris G‑A, Bui B, Banks M S, Drettakis G. (2017). “Accommodation and comfort in head‑mounted displays.” ''ACM Transactions on Graphics'', 36 (4): Art 87. doi:10.1145/3072959.3073622. https://doi.org/10.1145/3072959.3073622</ref> | |||
===Technological Solutions=== | |||
These hardware approaches aim to create displays where the accommodation distance can dynamically match the vergence distance demanded by the virtual content: | |||
{| class="wikitable plainrowheaders" | |||
! Approach !! Principle !! Representative prototypes / Research !! Strengths / Limitations | |||
|- | |||
! [[Varifocal display|Varifocal]] | |||
| [[Eye tracking|Eye-tracking]] determines the user's gaze depth, and the display system adjusts a single focal plane to match that depth using [[Tunable lens|tunable lenses]] (for example liquid crystal, liquid lens, Alvarez) or mechanically moving components (screen or lens). | Meta Reality Labs Butterscotch Varifocal (2023);<ref name="DisplayDaily2023">{{cite web |title=Meta’s Going to SIGGRAPH 2023 and Showing Flamera and Butterscotch VR Technologies |url=https://displaydaily.com/metas-going-to-siggraph-2023-and-showing-flamera-and-butterscotch-vr-technologies/ |website=Display Daily |date=2023-08-04}}</ref> UNC Wide-FOV deformable-mirror NED.<ref name="Dunn2017">Dunn D, Tippets C, Torell K, et al. (2017). “Wide field‑of‑view varifocal near‑eye display using see‑through deformable membrane mirrors.” ''IEEE TVCG'', 23 (4): 1322‑1331. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2017.2657058. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2017.2657058</ref> | |||
| Delivers correct focus cue at the depth of fixation. Challenges include eye-tracking latency and accuracy, depth switching speed, limited depth range, and potentially incorrect blur cues for objects not at the fixation depth.<ref name="UNC2019">{{cite web |title=Dynamic Focus Augmented Reality Display |url=https://telepresence.web.unc.edu/research/dynamic-focus-augmented-reality-display/ |website=UNC Graphics and Virtual Reality Group |year=2019}}</ref> | |||
|- | |||
! [[Multifocal display|Multifocal / Multiplane]] | |||
| Presents images on several fixed focal planes simultaneously (for example using stacked LCDs, beam splitters) or time-sequentially. Content is rendered on the plane closest to its virtual depth. | Stanford light-field HMD research;<ref name="Wired2015">{{cite web |last=Zhang |first=S. |title=The Obscure Neuroscience Problem That’s Plaguing VR |url=https://www.wired.com/2015/08/obscure-neuroscience-problem-thats-plaguing-vr/ |website=Wired |date=2015-08-11}}</ref> Magic Leap 1 (2 planes). | Provides more correct focus cues across multiple depths simultaneously without necessarily requiring eye-tracking. Challenges include complexity, cost, reduced brightness/contrast, potential visible transitions between planes, and limited number of planes. | |||
|- | |||
! [[Light field display|Light Field]] | |||
| Attempts to reconstruct the 4D light field of the scene (rays of light with position and direction). This allows the eye's lens to naturally focus at different depths within the reproduced volume. | Research using [[lenslet array]]s, parallax barriers, holographic optical elements, super-multi-view displays. | Potentially provides true continuous focus cues without eye-tracking. Challenges include extremely high resolution and bandwidth requirements, computational complexity, limited field of view, and tradeoffs between spatial and angular resolution. | |||
|- | |||
! [[Holography|Holographic Displays]] | |||
| Aims to fully reconstruct the wavefront of light from the virtual scene using diffraction patterns generated by [[Spatial light modulator|spatial light modulators]]. | Research by Microsoft Research, [[VividQ]], Light Field Lab. | Theoretically the ultimate solution, providing all depth cues including accommodation correctly. Challenges include high computational cost ("speckle" noise), limited field of view, and hardware complexity for real-time, high-quality HMDs. | |||
|- | |||
! [[Retinal projection|Retinal Projection / Scanning]] | |||
| Scans modulated light (often laser) directly onto the retina, potentially creating an image that is always in focus regardless of the eye's accommodation state (Maxwellian view). | Research systems; formerly North Focals (acquired by Google). | Can bypass VAC by eliminating the need for accommodation. Challenges include small [[Eyebox|eyebox]], potential for visual artifacts (for example [[Floater|floaters]] becoming more visible), safety concerns, and achieving high resolution/FOV. | |||
|- | |||
! Emerging Optics | |||
| Novel optical components like Alvarez freeform lenses,<ref name="Liu2024">Liu Y, Cheng D, Wang Y, Hua H. (2024). “A varifocal augmented‑reality head‑up display using Alvarez freeform lenses.” ''Journal of the Society for Information Display'', 32 (4): 310‑320. doi:10.1002/jsid.1286. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsid.1286</ref> tunable fluidic lenses, and deformable membranes are being explored for compact, low-power varifocal or multifocal elements. | Primarily research stage. | Aim for integration into smaller form factors. Manufacturing challenges, response time, optical quality, and control complexity remain active research areas. | |||
|} | |||
==Temporary Workarounds / Adaptation== | |||
* '''Closing One Eye''': Viewing with only one eye eliminates [[Binocular disparity|binocular disparity]] cues, thereby removing the vergence signal and the conflict. This can sometimes make it easier to focus on virtual objects, particularly near ones, at the cost of losing stereoscopic depth perception.<ref name="Kreylos2014VAC" /> | |||
* '''Optimal Optical Correction''': Ensuring users wear their correct [[Eyeglass prescription|prescription glasses]] or [[Contact lens|contact lenses]] minimizes any additional strain on the visual system from uncorrected [[Refractive error|refractive errors]]. | |||
* '''Adaptation''': The visual system can exhibit some adaptation to VAC during prolonged use, temporarily weakening the coupling between vergence and accommodation.<ref name="Kreylos2014VAC" /> However, this adaptation might be slow, incomplete, and can lead to the lingering aftereffects mentioned earlier when returning to natural viewing conditions. | |||
* | ==Current Research Frontiers== | ||
* '''High-Resolution Varifocal Displays''': Prototypes like Meta’s Butterscotch demonstrate progress towards retinal resolution (for example 60 pixels per degree) combined with reasonably fast depth switching, suggesting potential commercial viability.<ref name="DisplayDaily2023" /> | |||
* '''Focus-Correct Passthrough AR''': Integrating varifocal or multifocal optics into [[Video passthrough|video-see-through]] AR systems to correctly render both real-world and virtual imagery at appropriate focal depths.<ref name="UNC2019" /> | |||
* '''Standards and Health Implications''': Ongoing work by standards bodies (for example ISO TC159, IEC TC100) to develop guidelines for extended VR/AR use, particularly concerning children and workplace applications. | |||
* '''Perceptual Modeling''': Research using large-sample studies to better understand individual variability in the accommodation-vergence relationship, potentially enabling personalized comfort settings or adaptive display parameters.<ref name="Lin2022" /> | |||
* | ==See also== | ||
* [[Depth perception]] | |||
* [[Eye tracking]] | |||
* [[Light field display]] | |||
* [[Stereoscopy]] | |||
* [[Varifocal display]] | |||
* [[Vergence]] | |||
* [[Visual fatigue]] | |||
* [[Virtual Reality Sickness]] | |||
==References== | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Terms]] | [[Category:Terms]] | ||
[[Category:Technical Terms]] | |||
[[Category:Vision]] | |||
[[Category:Physiology]] | |||
[[Category:Display Technology]] | |||
[[Category:Human Factors]] | |||
[[Category:Visual Ergonomics]] | |||
[[Category:Virtual Reality]] | |||
[[Category:Augmented Reality]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:17, 2 July 2025
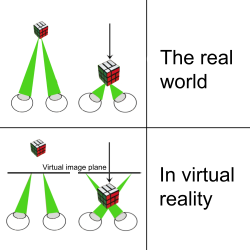
Vergence-accommodation conflict (VAC), also known as accommodation-vergence conflict or sometimes accommodation-vergence mismatch, is a visual and perceptual phenomenon that occurs when the brain receives mismatching cues between the distance to which the eyes are pointed or converged (vergence) and the distance at which the eyes' lenses are focused (accommodation).[1][2] Because natural viewing conditions tightly couple these two mechanisms, breaking that link is a primary cause of visual discomfort and performance issues in modern virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and other stereoscopic 3-D displays, including nearly all mainstream head-mounted displays (HMDs).[1]
Physiological Basis
When fixating on an object in the real world, the human visual system simultaneously performs two key actions:
- Vergence: The two eyes rotate inwards (convergence) or outwards (divergence) via the extraocular muscles so their lines of sight intersect at the target object, enabling single binocular vision. This response is primarily driven by retinal disparity.
- Accommodation: The ciliary muscle adjusts the shape and thus the optical power of the crystalline lens within each eye to bring the image of the target object into sharp focus on the retina. This response is primarily driven by retinal blur.
In natural vision, these two systems are tightly linked through fast, reciprocal neurological signals known as the accommodation-vergence reflex.[2][3] This coupling ensures that the eyes focus at the same distance they are pointed, allowing for clear, comfortable, and efficient vision. Stereoscopic displays disrupt this natural coupling because binocular disparity cues drive the vergence system to the simulated depth of a virtual object, while the accommodation system is driven by blur cues to focus on the physical display surface, which is typically at a fixed optical distance.[3]
Causes / Occurrence in Display Technologies
The vergence-accommodation conflict is inherent in display technologies where the perceived depth of content differs from the physical or optical distance of the display surface:
- Fixed-focus HMDs: Nearly all consumer VR and many AR headsets use internal display screens (like OLED or LCD) viewed through lenses. These lenses create a virtual image of the screens, making them appear to be located at a fixed focal distance, typically between 1.3 and 2 meters (though this varies).[4] Consequently, viewers must accommodate (focus their eyes) to this fixed plane to see a sharp image, regardless of the perceived depth of virtual objects. However, stereoscopic rendering creates virtual objects that appear at various depths by presenting slightly different images to each eye, requiring the viewer's eyes to converge or diverge (vergence). Objects rendered virtually nearer than the fixed focal plane induce a positive VAC (eyes converge more than they accommodate), while objects rendered virtually farther induce a negative VAC (eyes converge less than they accommodate).[5]
- 3D Cinema and Television: VAC also occurs here, but symptoms are often milder. The screen is typically farther away, the field of view is smaller, and content creators can limit disparities to keep virtual objects within a "zone of comfort" relative to the screen distance.[6]
- Optical See-Through (OST) AR: In OST AR glasses, virtual images (often at a fixed focus) are overlaid onto the real world. This creates a conflict not only between vergence and accommodation for virtual objects but also a potential mismatch between focusing on real-world objects at various distances and the fixed focus of the virtual overlay. This can introduce depth discontinuities, reduce the perceived registration accuracy of virtual objects, and cause discomfort.[7]
Effects and Symptoms
The sustained conflict between vergence and accommodation forces the visual system and brain to work harder, potentially leading to a range of negative effects:[3][1]
- Visual fatigue / Eyestrain: Tired, aching, or burning eyes resulting from the prolonged effort to resolve conflicting cues.
- Headaches.
- Blurred Vision: Difficulty maintaining sharp focus on virtual objects, especially those perceived as very near or very far relative to the display's fixed focal plane.
- Diplopia (Double Vision): Incorrect vergence responses due to the conflict can sometimes lead to seeing double images.
- Focusing Problems: Difficulty rapidly refocusing between virtual objects at different apparent depths because the natural reflex is disrupted. Users may also experience lingering focus issues or unusual visual sensations after removing the HMD.
- VR Sickness / Discomfort: VAC is considered a significant contributor to symptoms like nausea, dizziness, and general discomfort associated with VR/AR use.
- Reduced Visual Performance: Measurable degradation in tasks requiring fine depth judgments, reduced reading speed, slower visuomotor reaction times, and increased time required to fuse binocular images.[1][8]
- Focal Rivalry: Particularly in AR, the conflict between focusing on a real-world object and a virtual object projected at a different focal distance can make it difficult or impossible to see both sharply simultaneously.
The severity of these symptoms varies significantly between individuals and depends on factors such as the magnitude of the VAC (the difference between vergence and accommodation distances), the duration of exposure, the nature of the visual content, and individual visual capabilities. Conflicts below approximately 0.4 to 0.6 diopters are often tolerated, but larger conflicts, especially for near-field virtual objects (within arm's reach), become increasingly problematic.[5][6]
Measurement
VAC can be quantified by comparing the optical power (measured in diopters, D, which is the reciprocal of distance in meters) required for accommodation versus the optical power corresponding to the vergence distance.[3]
- `VAC (Diopters) = | (1 / Accommodation Distance (m)) - (1 / Vergence Distance (m)) |`
For example, if an HMD has a fixed focus set to 2 meters (requiring 1/2.0 = 0.5 D of accommodation) and displays a virtual object that appears to be 0.5 meters away (requiring 1/0.5 = 2.0 D of vergence), the VAC magnitude is |0.5 D - 2.0 D| = 1.5 D.
Mitigation Strategies
Addressing VAC is a major focus of VR and AR research and development. Strategies fall into two main categories: content design and technological solutions.
Content and Interaction Guidelines
Careful design can minimize VAC-induced discomfort in fixed-focus displays:
- Limit Depth Range: Keep critical interactive content and prolonged visual targets within the "zone of comfort," typically corresponding to less than ~0.6 D of VAC for foreground objects (closer than the focal plane) and ~1.0 D for background objects (farther than the focal plane).[6][5]
- Avoid Rapid Depth Changes: Avoid sudden disparity jumps (> 1 D) or rapid oscillations in depth for prominent objects. Allow the visual system time (at least 500 ms) to adjust to significant depth changes.[3]
- Optimize UI Placement: Present user interface elements, text, and critical information at or slightly behind the display's native focal plane where VAC is zero or negative (which is generally better tolerated).[5]
- Simulate Blur: When hardware cannot provide correct focus cues, incorporate gaze-contingent depth-of-field rendering (simulating blur for objects not being looked at) to provide monocular depth information that aligns better with vergence, potentially reducing cue conflicts.[9]
Technological Solutions
These hardware approaches aim to create displays where the accommodation distance can dynamically match the vergence distance demanded by the virtual content:
| Approach | Principle | Representative prototypes / Research | Strengths / Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Varifocal | Eye-tracking determines the user's gaze depth, and the display system adjusts a single focal plane to match that depth using tunable lenses (for example liquid crystal, liquid lens, Alvarez) or mechanically moving components (screen or lens). | Meta Reality Labs Butterscotch Varifocal (2023);[10] UNC Wide-FOV deformable-mirror NED.[11] | Delivers correct focus cue at the depth of fixation. Challenges include eye-tracking latency and accuracy, depth switching speed, limited depth range, and potentially incorrect blur cues for objects not at the fixation depth.[12] | |
| Multifocal / Multiplane | Stanford light-field HMD research;[13] Magic Leap 1 (2 planes). | Provides more correct focus cues across multiple depths simultaneously without necessarily requiring eye-tracking. Challenges include complexity, cost, reduced brightness/contrast, potential visible transitions between planes, and limited number of planes. | ||
| Light Field | Research using lenslet arrays, parallax barriers, holographic optical elements, super-multi-view displays. | Potentially provides true continuous focus cues without eye-tracking. Challenges include extremely high resolution and bandwidth requirements, computational complexity, limited field of view, and tradeoffs between spatial and angular resolution. | ||
| Holographic Displays | Aims to fully reconstruct the wavefront of light from the virtual scene using diffraction patterns generated by spatial light modulators. | Research by Microsoft Research, VividQ, Light Field Lab. | Theoretically the ultimate solution, providing all depth cues including accommodation correctly. Challenges include high computational cost ("speckle" noise), limited field of view, and hardware complexity for real-time, high-quality HMDs. | ||
| Retinal Projection / Scanning | Research systems; formerly North Focals (acquired by Google). | Can bypass VAC by eliminating the need for accommodation. Challenges include small eyebox, potential for visual artifacts (for example floaters becoming more visible), safety concerns, and achieving high resolution/FOV. | ||
| Emerging Optics | Primarily research stage. | Aim for integration into smaller form factors. Manufacturing challenges, response time, optical quality, and control complexity remain active research areas. |
Temporary Workarounds / Adaptation
- Closing One Eye: Viewing with only one eye eliminates binocular disparity cues, thereby removing the vergence signal and the conflict. This can sometimes make it easier to focus on virtual objects, particularly near ones, at the cost of losing stereoscopic depth perception.[2]
- Optimal Optical Correction: Ensuring users wear their correct prescription glasses or contact lenses minimizes any additional strain on the visual system from uncorrected refractive errors.
- Adaptation: The visual system can exhibit some adaptation to VAC during prolonged use, temporarily weakening the coupling between vergence and accommodation.[2] However, this adaptation might be slow, incomplete, and can lead to the lingering aftereffects mentioned earlier when returning to natural viewing conditions.
Current Research Frontiers
- High-Resolution Varifocal Displays: Prototypes like Meta’s Butterscotch demonstrate progress towards retinal resolution (for example 60 pixels per degree) combined with reasonably fast depth switching, suggesting potential commercial viability.[10]
- Focus-Correct Passthrough AR: Integrating varifocal or multifocal optics into video-see-through AR systems to correctly render both real-world and virtual imagery at appropriate focal depths.[12]
- Standards and Health Implications: Ongoing work by standards bodies (for example ISO TC159, IEC TC100) to develop guidelines for extended VR/AR use, particularly concerning children and workplace applications.
- Perceptual Modeling: Research using large-sample studies to better understand individual variability in the accommodation-vergence relationship, potentially enabling personalized comfort settings or adaptive display parameters.[8]
See also
- Depth perception
- Eye tracking
- Light field display
- Stereoscopy
- Varifocal display
- Vergence
- Visual fatigue
- Virtual Reality Sickness
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Hoffman D M, Girshick A R, Akeley K, Banks M S. (2008). “Vergence–accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue.” Journal of Vision, 8 (3): 33 (1‑30). doi:10.1167/8.3.33. PMID 18484839. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18484839/
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Kreylos, Oliver (2014-04-13). "Accommodation and Vergence in Head-mounted Displays". http://doc-ok.org/?p=1602.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Kramida G, Varshney A. (2016). “Resolving the vergence–accommodation conflict in head‑mounted displays.” IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 22 (7): 1912‑1931. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2015.2473855. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2015.2473855
- ↑ Kreylos, Oliver (2013-07-24). "Head-mounted Displays and Lenses". http://doc-ok.org/?p=1360.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Shibata T, Kim J, Hoffman D M, Banks M S. (2011). “The zone of comfort: Predicting visual discomfort with stereo displays.” Journal of Vision, 11 (8): 11. doi:10.1167/11.8.11. PMC 3369815. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3369815/
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 International Organization for Standardization. (2015). ISO 9241‑392:2015 - Ergonomics of human‑system interaction – Part 392: Ergonomic requirements for the reduction of visual fatigue from stereoscopic images. https://www.iso.org/standard/60317.html
- ↑ Zhou Y, Li X, Yuan C. (2021). “Vergence‑accommodation conflict in optical see‑through display: Review and prospect.” Results in Optics, 5: 100160. doi:10.1016/j.rio.2021.100160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rio.2021.100160
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Lin C‑J, Chi C‑F, Lin C‑K, Chang E‑C. (2022). “Effects of virtual target size, position and parallax on vergence‑accommodation conflict as estimated by actual gaze.” Scientific Reports, 12: 20100. doi:10.1038/s41598‑022‑24450‑9. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598‑022‑24450‑9
- ↑ Koulieris G‑A, Bui B, Banks M S, Drettakis G. (2017). “Accommodation and comfort in head‑mounted displays.” ACM Transactions on Graphics, 36 (4): Art 87. doi:10.1145/3072959.3073622. https://doi.org/10.1145/3072959.3073622
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Meta’s Going to SIGGRAPH 2023 and Showing Flamera and Butterscotch VR Technologies". 2023-08-04. https://displaydaily.com/metas-going-to-siggraph-2023-and-showing-flamera-and-butterscotch-vr-technologies/.
- ↑ Dunn D, Tippets C, Torell K, et al. (2017). “Wide field‑of‑view varifocal near‑eye display using see‑through deformable membrane mirrors.” IEEE TVCG, 23 (4): 1322‑1331. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2017.2657058. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2017.2657058
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Dynamic Focus Augmented Reality Display". 2019. https://telepresence.web.unc.edu/research/dynamic-focus-augmented-reality-display/.
- ↑ Zhang, S. (2015-08-11). "The Obscure Neuroscience Problem That’s Plaguing VR". https://www.wired.com/2015/08/obscure-neuroscience-problem-thats-plaguing-vr/.
- ↑ Liu Y, Cheng D, Wang Y, Hua H. (2024). “A varifocal augmented‑reality head‑up display using Alvarez freeform lenses.” Journal of the Society for Information Display, 32 (4): 310‑320. doi:10.1002/jsid.1286. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsid.1286

